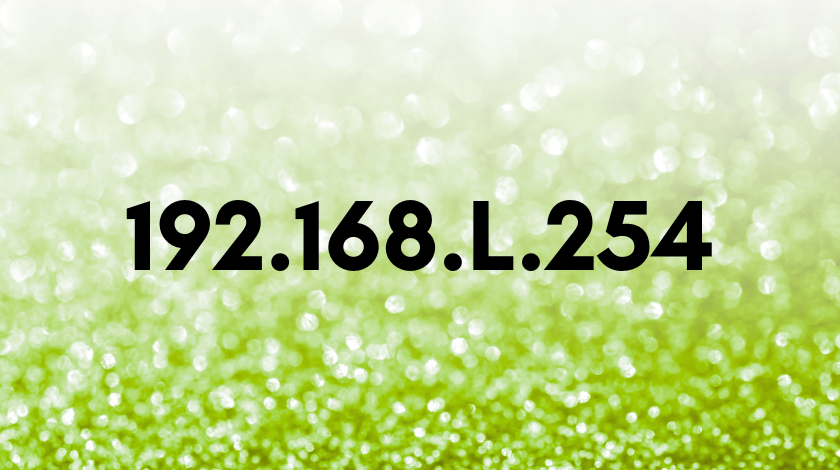In the invisible architecture of your home or office network, a single sequence of numbers acts as the master key: 192.168.1.254. Typed into a web browser, this private IP address is the gateway to your router’s or modem’s administrative panel, the command center from which your digital world is managed. This article explores the significance of this address, common login issues and their solutions, essential configuration tasks, and crucial security practices to ensure your network remains both efficient and secure.
Understanding the Address: Why 192.168.1.254?
To comprehend 192.168.1.254, one must first understand private IP addressing. The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) reserves specific address ranges for use on private networks, isolated from the public internet. The most common range is 192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.255. Your router acts as a traffic director, assigning unique private IPs (like 192.168.1.10) to each device (laptop, phone, smart TV) on your Local Area Network (LAN).
The router itself needs a static, unchanging address within this range—the default gateway. Manufacturers like AT&T (for many U-verse gateways), Linksys, D-Link, and others often use 192.168.1.254 as this default. It’s less common than the ubiquitous 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1, making it a memorable alternative for certain hardware. Accessing it grants you administrative privileges over the device that connects your private realm to the vast public internet.
Gaining Access: The Login Process and Common Hurdles
Accessing your router’s interface is straightforward but can be thwarted by minor issues. Follow this standard procedure:
-
Connect to the Network: Ensure your computer or smartphone is connected to the router’s network via Wi-Fi or an Ethernet cable.
-
Open a Browser: Launch Chrome, Firefox, Safari, or Edge.
-
Enter the Address: Type
http://192.168.1.254or simply192.168.1.254into the address bar and press Enter.
This is where users often encounter the first roadblock. If the page fails to load, troubleshoot using these steps:
-
Check the Connection: Verify your device is connected to the correct network.
-
Verify the Address: A critical and common typo is using the letter
linstead of the number1(e.g.,192.168.l.254). Always use numeric digits. Also, ensure you are not usinghttps://unless specified. -
Find Your Gateway: If the address is incorrect, discover your router’s true default gateway. On Windows, open Command Prompt and type
ipconfig; look for “Default Gateway.” On a Mac, go to System Settings > Network > Details > TCP/IP. -
Bypass Cache: Try a private/incognito browsing window to avoid cached page errors.
-
Hard Reset: As a last resort, use a paperclip to press the router’s tiny reset button for 10-15 seconds. Warning: This will erase all custom settings, restoring the device to factory defaults, including the default address
192.168.1.254.
Once the login page loads, you will need credentials. These are almost always printed on a label on the router itself—look for “Admin Username” and “Admin Password.” Common defaults are admin/admin, admin/password, or admin with a blank password. If these don’t work and you’ve never changed them, a hardware reset is necessary.
The Power Within: Essential Configuration Tasks
Upon successful login, you enter a dashboard that varies by manufacturer but generally offers control over these key areas:
-
Internet/WAN Settings: Configure the connection type (PPPoE, Dynamic IP, Static IP) as provided by your Internet Service Provider (ISP).
-
Wi-Fi Settings (Wireless): This is where you customize your network’s SSID (the visible name), select the security protocol (always choose WPA2 or WPA3), and set a strong, unique password. You can also select the broadcast channel to avoid interference from neighboring networks.
-
LAN Settings: Configure the DHCP server, which automatically assigns IP addresses to your devices. You can adjust the address pool and lease time here.
-
Firewall & Security: Enable the built-in firewall, set up access controls, and manage port forwarding or triggering for specific applications or games that require external connections.
-
Connected Devices: View a list of all devices currently using your network—a useful tool for spotting unauthorized intruders.
-
Firmware Updates: One of the most critical sections. Router manufacturers release firmware updates to patch security vulnerabilities, improve performance, and add features. Regular checks here are vital for network health.
Fortifying Your Digital Frontier: Security Imperatives
With great power comes great responsibility. The router admin panel is a prime target for attackers. Adhering to these security practices is non-negotiable:
-
Change Default Credentials Immediately: The single most important step. Leaving the default username and password is like locking your front door but leaving the key in the lock. Create a strong, unique admin password.
-
Disable Remote Administration: This feature, if enabled, allows you to access the admin panel from outside your home network. For 99% of users, this is an unnecessary and severe security risk. Ensure it is turned off.
-
Keep Firmware Updated: As mentioned, outdated firmware is a leading cause of compromised routers. Enable automatic updates if available, or set a quarterly reminder to check manually.
-
Use Robust Wi-Fi Encryption: Never use outdated WEP or WPA (TKIP) encryption. Enforce WPA2-PSK (AES) or, if supported by all your devices, WPA3.
-
Create a Guest Network: For visitors and smart home devices, a separate guest network with its own password isolates them from your main devices (like your personal computer and NAS), limiting potential damage if one is compromised.
Conclusion
The unassuming string of numbers—192.168.1.254—is far more than a technical footnote. It is the virtual address of your network’s headquarters, the control panel for the gateway between your private digital life and the global internet. Understanding how to access it, navigate its interface, and wield its tools is a fundamental aspect of modern digital literacy. It empowers you to solve connectivity problems, optimize performance for streaming and gaming, and, most critically, erect and maintain the security walls that protect your personal data from an ever-expanding array of online threats.
The journey from encountering a login error due to a simple typo like “192.168.l.254” to confidently updating firmware and configuring a guest network marks a transition from a passive user to an informed network administrator. In an era where our homes are filled with connected devices, from phones to thermostats, taking proactive ownership of this small piece of digital real estate is not just advisable; it is essential. Your router is the first and most important line of defense in your connected world. By mastering its access point, you ensure that your network remains a secure, efficient, and private foundation for your digital existence.